Description
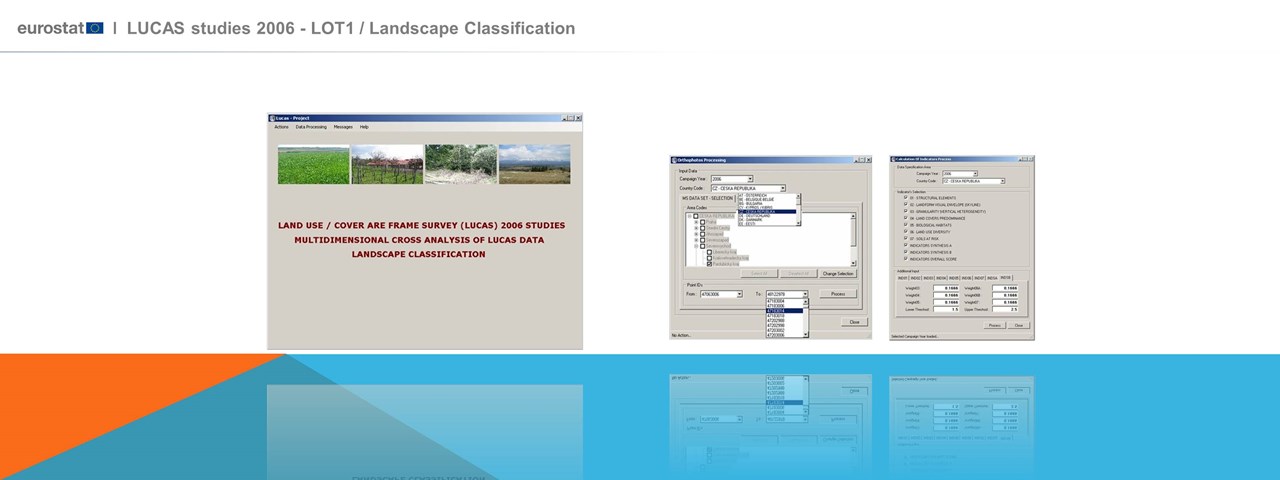
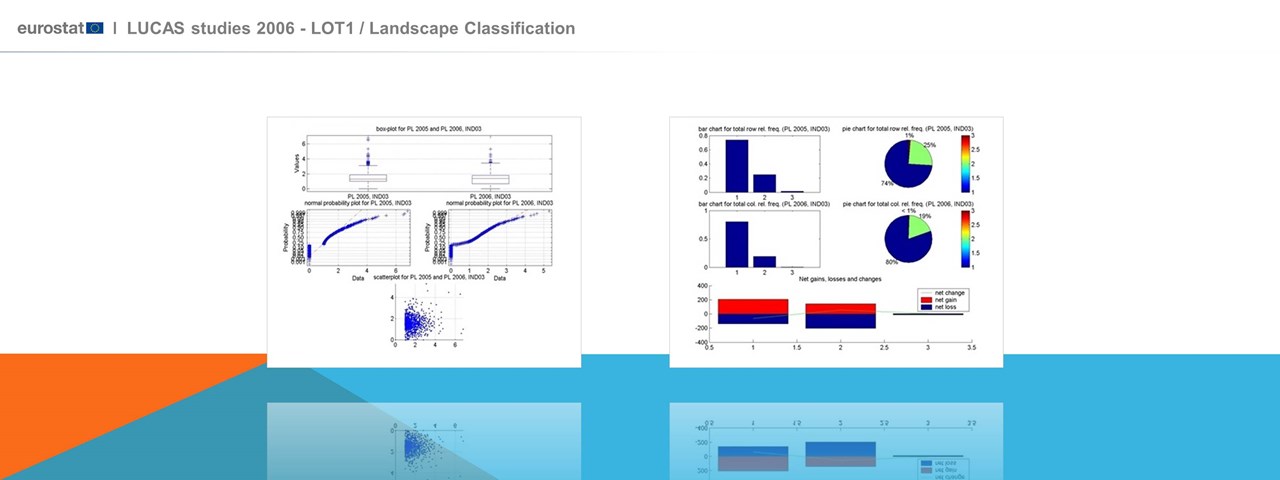
Design and Development of a Geographic Information System Development for systematic monitoring of landscape changes, through using geo-spatial data and landscape assessment indicators (landscape indicators) for the entire European continent. Implementation of innovative methods and optimized use of LUCAS data (orthophotos, field images, etc.).The project objective being to further develop a set of meaningful landscape indicators across Europe, through deploying innovative state of the art methods for optimizing the usage of the whole of the data of the LUCAS campaigns (orthophotos, landscape photos, etc). The project focused in exploiting the LUCAS data set, which covers (with some exceptions) the whole of the European territory and refers to information that is collected (annually) with common specifications and quality level (objectivity and precision of the information).
A high-level expert scientific group on landscape characterization has been set up to provide advice and guidance to the work as well as their opinion on the project results and findings. The outcome of an in depth analysis of the state of the art and the available data sets has guided the project orientation and developments. The analysis has pointed out the strengths and the weaknesses of the existing data sets towards establishing a systematic monitoring scheme of the European landscape and in this context the design of the indicators and the necessary implementations accounted for the data specificity as well as for future enhancements in their quality. The landscape classification accounted for the LANMAP2 categorization of the European landscapes and in this frame the access (for internal use only) to the LANMAP2 data set was secured for the consortium partners and for EUROSTAT. The project implementation and system performance demonstration was based on the data of a number of sample sites (11 areas (NUTS Level 3) of the following Member States: Spain (1), Italy (2), France (2), Hungary (1), Luxembourg (1), Poland (2), Czech Republic (1) and Slovenia (1).
A performant Software Quality Assurance Plan was also developed and applied to set up the SW specifications and to monitor the evolution and performance at the various stages of the development.